Algae Rhodophyta Phaeophyta Chlorophyta
INTRODUCTION: In this chapter Algae Rhodophyta Phaeophyta Chlorophyta will discuss in detail. Thallophyta comprises undifferentiated plants. Only algae include in the Thallophyta division. Accessory spores are responsible for asexual reproduction.
Characteristic Features:
- Algae are found in fresh water and marine. Few algae also occur on trees, moist soil, etc.
- It having an undifferentiated body it can be colonial, parenchymatous, or unicellular.
- Vascular tissues are not present.
- Mostly found in aquatic algae do not require water conduction.
- Mechanical tissue is not present.
- Photosynthetic is the mode of nutrition.
- Algae having chlorophyll, xanthophyll, and carotene.
- Isogamy, anisogamy, and oogamy for sexual reproduction.
- Mitospores and meiospores are responsible for asexual reproduction.
- Haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic are life cycle of algae.
 |
| Image 1: Algae |
- Mostly they are marine and autotrophic.
- The plant may be unicellular, parenchymatous, Filamentous.
- Cell wall contains Pectic compounds, Cellulose and Phycocolloids.
- Chlorophyll, Phycoerythrin, Phycocyanin, and Carotenoid photosynthetic pigments are present.
- Calcium carbonate is present all over the walls.
- Chromatophores are present.
- Due to the presence of phycoerythrin algae show red in color.
- Floridian Starch is a food reserve.
- Carpospores, neutral spores, tetraspores take place in asexual reproduction.
- Antheridium is the male sex organ and Carposporophyte is the female sex organ.
- Haploid and diploid is an alternation of generation.
 |
| Image 2: Red Algae |
Example of Red Algae:
- Polysiphonia: It is a marine alga. Long and Dwarf branches contain a plant. A plant is fixed by Rhizoid and Holdfast. The male sex organ is Antheridia and Carpogonia is the female sex organ. Carposporophyte is developed after fertilization. Carpospore is produced tetrasporophyte.
- Porphyra: It is a marine alga. Neutral spores help in asexual reproduction. The diploid Zygote is formed by sexual reproduction.
- Gelidium: Attached by a number of rhizoids. It is used in Agar formation.
- Batrachospermum: It is also known as a Frogspawn alga. Monospores help in asexual reproduction. Spermatangia is a male sex organ and Carpogonia is a female sex organ.
- Porphyra, Chondrus, etc. algae used as food.
- Agar is used as culture media.
- Carrageenin is used in toothpaste, leather finishing.
- Gloiopeltis used in textiles and paper.
- Corallina helps cure infections.
- Polysiphonia shows anti-bacterial activities.
Phaeophyta: Brown Algae
- It is Marine algae and is found in colder seas.
- Unicellular forms are not present.
- A plant body is divided into holdfast, stipe, and frond.
- Air vesicles are present and provide buoyancy.
- Cell walls having saccharides, cellulose, and phycocolloids.
- Photosynthetic pigments are Chlorophyll, Fucoxanthin, and Phycocolloid.
- Photosynthetic organelles are present.
- Carbohydrates and lipids are food reserve materials.
- Motile and Nonmotile spores help in Asexual reproduction.
- Isogamy, oogamy, and anisogamy help in sexual reproduction.
- Conduction of food materials by conducting tubes.
 |
| Image 3: Brown Algae |
Examples of Brown Algae:
- Dictyota: They develop in shallow water. Hairs are present on the surface of the frond. The diploid zygote is formed by fertilization.
- Sargassum: It is used as fodder and manure. Floating and attached forms are found. It shows antimicrobial activities. Holdfast, main axis, and lateral are the parts of a plant. Air bladders are present.
- Fucus: It is the source of fodder and manure. Pneumocysts and conceptacles are present.
- Laminaria: It is large size alga about 1-3 meters. It is used as food, manure, and iodine.
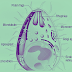
- Ectocarpus: It is a marine alga. Prostate portion and rhizoids help in plant fixation.
 |
| Image 4: Life Cycle of Ectocarpus |
Economic Importance of Brown Algae:
- Laminaria, Sargassum, Macrocystis, etc. are used as edible algae.
- Iodine is present in Fucus and Laminaria.
- Potash is found in Macrocystis and Nereocystis.
- Laminaria show antibiotic activities.
- Durvillea show vermifuge properties.
See also: Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes
Biological Classification
Protista Protozoan Plasmodium
Chlorophyta: Green Algae
- It is a group of Eukaryotes.
- Mostly found in freshwater.
- They Found or moist soil, trees, and walls.
- The cell wall is made up of cellulose.
- They are unicellular.
- Chloroplast is present.
- Chlorophyll, Carotenoid, and Xanthophylls are photosynthetic pigments.
- Due to the presence of chlorophyll algae show green color.
- Mitospores and meiospores help in asexual reproduction.
- Isogamy, anisogamy, and oogamy help in sexual reproduction.
- The life cycle occurs as Haplontic, diplontic and diplohaplontic.
 |
| Image 5: Green Algae |
1. Chlamydomonas:
- It is a Eukaryotic and biflagellate alga.
- It is found in fresh water and marine.
- The cell wall is made up of Glycoprotein.
- For osmoregulation, contractile vacuoles are present.
- Alga contains a nucleus.
- Zoospores, hypnospores and aplanospores help in asexual reproduction.
- Flagellate spores are in zoospores.
- Hypnospores having thick-walled and Aplanospores having thinly walled.
- Zygotic meiosis forms four haploid zoospores.
- It is an unbranched.
- Central vacuoles are present.
- Chloroplast is present.
- Fragmentation help in vegetative reproduction.
- Zoospores, hypnospores, aplanospores help in asexual reproduction.
- Biflagellate and tetraflagellate zoospores are motile.
- Hypnospores having thick-walled and aplanospores having thin-walled spores.
- Isogamous helps in sexual reproduction.
- The formation of a zygote is indirect.
- It is unbranched.
- It is found in freshwater.
- Cells are green.
- Cells capable of division.
- A single nucleus is present.
- Fragmentation help in vegetative reproduction.
- Conjugation help in sexual reproduction.
- Conjugation occurs by scalariform and lateral.
- The formation of the zygote is direct.
- It is found in freshwater.
- The male sex organ is antheridium and the female sex organ is oogonium.
- Fragmentation help in vegetative reproduction.
- It is used as food for several livings.
- It is used as manure.
- It is found in freshwater.
- It contains approx. 500 to 60,000 cells.
- The posterior region cells are large.
- During the swimming, it performs rotation.
- Formation of daughter colonies by asexual reproduction.
- Oogamous help in sexual reproduction.
- Ulva, Chlorella, Caulerpa contains minerals, lipids, and vitamin used as a food.
- Caulerpa and Chlorella are used as Antibiotics.
Conclusion: Algae are classified under the plant kingdom and characterized without embryo stage. Algae differentiated the basis of pigments and product storage.
This is the full article on Algae Rhodophyta Phaeophyta Chlorophyta.











0 comments:
Post a Comment