Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes
INTRODUCTION: In this chapter, Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes we will discuss in detail. Fungi is Non-vascular, achlorophyllous, spore-forming.
- Fungi is cosmopolitan.
- Present in water, air, and living organisms.
- Fungi contain chitin.
- Its food reserve is Glycogen.
- Mycology: Study of fungi.
- The mode of nutrition is Heterotrophs.
- Chlorophyll is absent hence not able to prepare their food.
- Saprotrophic fungi obtain food from dead and waste material.
 |
| Image 1: Fungi |
Fungal Structure:
- The Body having tubular filaments i.e., Hyphae.
- The filamentous hyphae or mass of hyphae is known as mycelium.
- In yeast mycelium is absent.
- Fungi have vegetative and reproductive phases.
 |
| Image 2: Formation of Mycelium |
Protista Protozoan Plasmodium
Tissue and Cell Structure:
- When hyphae are held together called Plectenchyma it contains Prosenchyma ( loosely hyphae), and Pseudoparenchyma ( closely packed hyphae).
- When single nuclei are present condition is monokaryotic.
- When two nuclei are present condition is dikaryotic.
- Chitin is made up of acetyl glucosamine.
- Plastids are absent.
- Mitochondria, Endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, microtubules, etc. are present.
- Food reserve is glycogen and oil.
 |
| Image 3: Rhizopus |
Reproduction:
1. Sexual reproduction: Involves Karyogamy, plasmogamy, and meiosis.
- Homothallic: when mating occurs between the genetically are similar.
- Heterothallic: when mating occurs between two genetically are different.
- Union of cytoplasm i.e., Plasmogamy, and union of Nuclei i.e., Karyogamy.
- The stage between plasmogamy and karyogamy contains two nuclei (dikaryon).
- Sexual reproduction methods: Plano gametic Copulation: Heterogamous fusion can be Oogamy and anisogamy.
- Gametangial Contact: Male gamete antheridia transfer to female gamete oogonia by fertilization tube.
- Gametangial Copulation: Formation of zygospore.
- Spermatogamy: Male cell carried to the receptive region of the female sex organ.
- Somatogamy: Reproduction occurs by the fusion of two hyphae.
 |
| Image 4: Sexual Reproduction in Fungi |
- Budding: Bud is arising on the parent body. Budding occurs in yeast and many other fungi.
- Fragmentation: By mechanical reason or much other reason parent body breaks up into two or several segments and form a complete organism. Fragmentation occurs in Rhizopus.
- Fission: Yeast divide two or more daughters identical to the parent.
 |
| Image 5: Vegetative Reproduction in fungi |
- Occurs by the formation of spores. They can be motile or non-motile. Sexually produced spores are ascospores, basidiospores and others are asexually produced spores.
- Zoospores: Spores are naked and motile. Flagella help in swimming. Examples: Phytophthora, Albugo, etc.
- Sporangiospores: They are non-flagellate and dispersed by air. Examples: Mucor, Rhizopus, etc.
- Conidia: Spores are non-motile and develop by special hyphae. Example: Penicillium, Aspergillus, etc.
- Chlamydospores: Spores are thick-walled and develop by the accumulation of protoplasm.
- Basidiospores: They are non-motile and develop from basidium.
- Oidia: Produce during excess water and particular salts. Example: Rhizopus etc.
- Ascospores: Spores are non-motile and produce inside asci.
 |
| Image 6: Fungal Spores |
Fungus Classification:
 |
| Image 7: Kingdom Fungi |
PHYCOMYCETES:
- Sexual and Asexual reproduction occurs.
- Phycomycetes divide into two groups i.e., oomycetes and zygomycetes.
- Spore formation occurs by asexual reproduction.
- Biflagellate zoospores, non-flagellate gametes, and smooth flagella are present.
- Antheridium passes into oogonium by a fertilization tube.
- Examples: the late blight of potato caused by➡ Phytophthora infestans.
- Mostly saprotrophic, zoospores are absent.
- Non motile Mitospores are present.
- Gametangial copulation for the sexual reproduction.
- Gametes are multinucleate.
- Examples: Soft rot of Apple, strawberry is due to Rhizopus.
 |
| Image 8: Zygomycetes |
- Rhizopus is a black bread mold.
- It is saprotrophic.
- Hyphae are rhizoidal, sporangiophores, stoloniferous, and zygophores.
- Rhizoidal hyphae are branched, sporangiophores are unbranched, stoloniferous are unbranched and zygophores are subaerial.
- Fragmentation for vegetative reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction by sporangiospores, chlamydospores, and oidia.
- Sporangiospores: Sporangiophore develops ➡ sporangium.
- chlamydospores: chlamydospores rise ➡ new mycelium.
- Oidia: They multiply by➡ budding.
- Sexual reproduction: Rhizopus stolonifer is heterothallic. Trisporic acids help in the formation of zygophores. Two gametangia are dissolves and two coenogametes form diploid zygote and zygospore. Germ sporangium develops germ spores.
ASCOMYCETES:
- They are pigmented moulds.
- Septate hyphae are present.
- Cell wall having chitin.
- Budding and fission for asexual reproduction.
- Conidiophores can be branched or unbranched.
- Sexual reproduction by sex cells, gametangial between antheridium and ascogonium.
- Plasmogamy and karyogamy for fertilization.
- Ascospores produce an ascus. The asci form ascocarps.
Yeast:
- They are nonmycelial or pseudomycelial.
- Mode of asexual reproduction in yeasts: Fission yeasts, budding yeasts, and halobial yeasts.
- Ascus formation is known in yeasts.
- Yeasts are unicellular and form temporary chains during rapid growth.
- It contains chitin and mannan β glucan.
- The mode of nutrition is saprotrophic.
- Budding and fission occur in asexual reproduction.
 |
| Image 9: Life cycle of Yeast |
Economic importance of Yeast:
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used in baking food.
- Saccharomyces ellipsoidens are used in the brewing industry.
- Yeast is also used in vitaminized food.
- Some yeast is used in the silk industry.
Aspergillus:
- It contaminates bread, jellies, cheese, and laboratory cultures.
- It is rotting the cigars, figs, and many fruits.
- It also causes ear infections.
- It is commercial antibiotics.
- It spoils citrus food, paper, apple, and other products.
- It helps in the formation of organic acids.
BASIDIOMYCETES:
- It is club fungi.
- Motile cells are not present.
- Primary and Secondary mycelia are present.
- Sex organs do not involve during sexual reproduction.
- Primary mycelium and Secondary mycelium are monokaryotic, dikaryotic respectively.
- Basidium can be septate or aseptate.
- A basidium produces four basidiospores.
 |
| Image 10: Basidiomycetes |
Mushroom:
- Agaricus campestris is edible.
- The mode of nutrition is saprotrophic.
- Primary mycelium and Secondary mycelium are present but secondary is long-lived.
- Clamp connections show by secondary mycelium.
- Secondary mycelium gives rise mass of hyphae during favorable conditions.
- Stipe is fleshy and its base is swollen.
- Pilus is circular, looking like an umbrella.
- Basidiocarp produces several spores.
- They are non-edible.
- Toadstools contain poison.
- Having white spores.
- Example: Amanita muscaria etc.
- They produce black spores known as smut spores.
- Spores are exposed in loose smut and spores are not exposed in covered smut.
- The sexual stage is not known in this class.
- They are unicellular.
- Conidia help for asexual reproduction.
- Examples: Trichoderma, Early blight, Wilts, Arthrobotrys, Red rot, Tikka disease, etc.
Tikka Disease:
- Black and brown spots occur in groundnut leaves.
- Filamentous and septate conidia are present.
Red Rot:
- Midribs of leaf and canes effects by Colletotrichum falcatum, cause red rot in sugarcane.
- It decreases the juice content.
Wilts:
- Banana, Potato, Cotton wilts by Fusarium.
- Chlamydospores, macroconidia, and microconidia spores show by Fusarium oxysporum.
Early Blight:
- Causes occur in Potato and Tomato.
- Causal organism is Alternaria solani.
- Brown spots develop in the leaf.
- Branch and leaf are falls.
Lichens:
- It is the association of fungus and alga.
- The algal partner is a cyanobacterium.
- Lichen grows in alpines, tree bark, roofs, etc.
- Lichen's colors have green, orange, greyish, black, or brown.
- Alga performs photosynthesis activity.
- The fungus has minerals and water that are used by alga for the preparation of food.
 |
| Image 11: Lichens |
Importance of Lichens:
- They are used in dyes.
- Ramalina is used in Perfumes.
- Lichen use as colonisers.
- Usnea and Cladonia are used for medicinal purposes.
Mycorrhizae:
- Mutual beneficial of fungus and Root of higher plants.
- Absence of Root hairs and Root cap in these plants.
- Ecto mycorrhizae lie on the Root surface in bulk.
- Endo mycorrhizae lie on the Root surface in little.
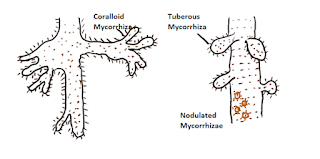 |
| Image 12: Mycorrhizae of Pinus |
This article contains Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes with images for better understanding
See Also: Diversity Living World











0 comments:
Post a Comment