Protista Protozoan Plasmodium
INTRODUCTION: In this chapter, Protista Protozoan Plasmodium will discuss in detail. Protozoans were firstly studied by Leeuwenhoek in 1677.
Characteristics features of Protozoan Protists:
- Habitat can be freshwater or marine.
- They are small, acellular, and calcareous.
- Pseudopodia, flagella, and cilia are Locomotory organs.
- Osmoregulation occurs by contractile vacuoles.
- Having radial or bilateral symmetry.
- The mode of nutrition is Holozoic.
- Reproduction occurs asexual or sexual.
- During adverse conditions, they form cysts for survival.
- Ammonia is a metabolic waste.
Mastigophora, Sarcodina, Sporozoa, and Ciliata
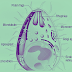
1. Group: Mastigophora: (Zooflagellate)
- The outer covering is a pellicle.
- Asexual reproduction occurs by Binary fission.
- The locomotory organ is the flagella.
- Association is commensals or symbionts.
- E.g. Trypanosoma gambiense, Leishmania donovani, Giardia intestinalis, etc.
- Sleeping sickness parasite.
- Transmit by blood-sucking Glossina palpalis.
- It is present in blood plasma in humans.
- It makes the unconscious.
- Cause black sickness.
- Also occurs anemia, effects on liver and spleen.
- Transmit by Phlebotomus argentipes.
- It is common in India and America.
 |
| Image 1: Zooflagellates |
- Effects the women's vagina.
- It causes leucorrhoea disease.
- Transmission occurs by food and water.
- It affects the part of the small intestine.
- It also causes diarrhea, head pain, epigastric pain, increases body temperature, etc.
- Locomotion by the Pseudopodia.
- Found in fresh and seawater.
- Nutrition is holozoic.
- Asexual and sexual reproduction takes place.
- E.g. Amoeba proteus, Entamoeba histolytica, Globigerina etc.
SEE ALSO: Protista Photosynthetic Dinoflagellates Euglenoids |
- Locomotion occurs by Lobo podia.
- Osmoregulation occurs by the contractile vacuole.
- Holozoic is the mode of nutrition.
- Contractile vacuole works faster in distilled water.
- Having Mitochondria.
- The life cycle is monogenetic.
- The disease is known as amoebiasis.
- Contractile vacuole is not present.
- It affects the large intestine and forms ulcers.
- Abdominal pain was also reported.
- It has two forms i.e., Magna and minuta
- Effective medicine to kill this causal organism is Metragyl or Flagyl.
 |
| The life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica |
- Mostly found in marine.
- For locomotion pseudopodia are present.
- Protoplasm is differentiated.
- Reproduction occurs by binary fission.
- Examples: Acanthometra and Collozoum.
- Found in fresh and marine water.
- For creeping and ingestion pseudopodia are present.
- Reproduction occurs through binary and multiple fission.
- Examples: Globigerina and Elphidium.
- Contains axopodia.
- Scales and spines having on the skeleton.
- Example: Actinophrys etc.
- They are endoparasite.
- Locomotory organelles are not present.
- Contractile vacuoles is not present.
- Sexual reproduction by syngamy.
- The Mode of Nutrition is Parasitic.
- E.g. Plasmodium, Monocystis, Eimeria, etc.
a) Human beings: Inhuman, malarial parasites reproduce asexually.
b) Female Anopheles Mosquito: Malarial parasites reproduce sexually.
A) Life cycle of Plasmodium in Human: Infection occurs by Sporozoite.
- Pre-erythrocytic Schizogony: When sporozoite becomes rounded known as schizont.
Schizont → multiply and → form Crypto zoites → moves into sinusoids (in the liver).
- Exo-erythrocytic Schizogony: Crypto zoites → Form Meta cryptozoites.
- Erythrocytic Schizogony: Schizogony in the RBC is known as Erythrocytic Schizogony.
- Young Trophozoite: When Metacryptozoite moves into RBCs they become round and this stage is known as Young Trophozoite.
- Amoeboid Stage: When Vacuole is disappeared and these Trophozoites change the shape i.e., amoeba-shaped. Trophozoites acquire hemozoin granules they derived from Erythrocytes. Haemoglobin having protein and iron parts.
- Formation of Merozoites: Trophozoite perform mitotic division and form merozoites. RBC releases merozoites in human blood and appears symptoms of fever known as the Incubation period. Symptoms of Malaria: Fever, chilliness, headache, muscular pain, etc.
- Formation of Gametocytes: Some Merozoites form gametocytes, these form Smaller gametocytes and Larger gametocytes.
- Female Anopheles suck the blood from infected human and gametocytes comes into the lumen of mosquito.
- The formation of gametes is known as Gametogony.
- Formation of Zygote i.e., Fertilization.
- The encyst zygote known as Sporont.
- The nucleus of the oocyte divides and forms small haploid nuclei.
 |
| The life cycle of Malarial Parasite |
- Elimination of Mosquitoes: Mosquitoes killed by D.D.T, Flit, etc.
- Destruction of larvae.
- Breeding grounds of larva should be drained.
- Develop the number of cilia during the life cycle.
- A pellicle is the outer covering of ciliate protozoans.
- They live in fresh and marine water.
- Locomotory organs are cilia.
- The contractile vacuole is present for osmoregulation.
- The mode of nutrition is Holozoic.
- Asexual and sexual reproduction takes place.
- Examples: Paramecium, Balantidium, Vorticella, etc.
- Found in freshwater.
- It is a surface feeder.
- The mode of nutrition is microphageal.
- The shape is like a Slipper.
- Outer covering pellicle maintains the shape of the body.
- It having macronucleus and micronucleus.
- It having a contractile vacuole for osmoregulation.
- Transverse binary fission method for asexual reproduction.
- Conjugation and autogamy method for sexual reproduction.
- Sensitive Paramecia: Having no kappa particles and do not produce poisonous substances.
- Killer Paramecia: Having kappa particles and secretes paramecin.
- Found in the large intestine of humans.
- Causes diseases like diarrhea, ulceration, etc.
- Transmission through contaminated water and food.
|
S.NO. |
Parasite |
Distribution |
Habitat |
Disease cause |
Transmission |
|
1 |
Trypanosoma
gambiense |
Central
Africa |
Blood, cerebrospinal
fluid |
Gambium
sleeping sickness |
By Glossina
palpalis |
|
2 |
Trypanosoma
cruzi |
South America |
Blood |
Chagas
disease |
By Faeces of
bugs (triatomid) |
|
3 |
Leishmania donovani |
India |
Lymph glands,
Liver, Spleen |
Kala-azar |
By bites of Phlebotomus
argentipes |
|
4 |
Giardia
intestinalis |
World-wide |
Small
intestine |
Diarrhea |
By food and
water |
|
5 |
Trichomonas
vaginalis |
World-wide |
Vagina |
Leucorrhoea |
Sexual
intercourse |
|
6 |
Entamoeba
histolytica |
World-wide |
Large
intestine |
Amoebic
dysentery |
By food and
drink |
|
7 |
Leishmania
brasiliensis |
Asia and
Africa |
Nose, Mouth,
Pharynx |
Mucocutaneous
Leishmaniasis |
By sandfly |
Table 1: Pathogenic Protozoans in Human being
SEE ALSO: Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes














0 comments:
Post a Comment